A review with a backstory.
Last summer, I did a flying gig that started in Spokane and had me flying over a good portion of the state. The client was a video production company based in the U.K. that was working on a NOVA documentary about the ice age floods, which are often referred to as the Missoula Floods.
If you don’t know anything about the Missoula Floods, here’s the short version. Millions of years ago, when the Cascades were a chain of active volcanos, they laid down layer after layer of lava that became (mostly) basalt rock. The Ice Ages came and a sheet of ice stretched from the North Pole down into the northern United States. In Montana, the ice sheet formed a dam across the mouth of a valley and huge volumes of water accumulated behind it. Over time, the ice dam was eroded and broke free, releasing all that water very quickly. It came downstream, across Idaho and Washington State, carving out some very interesting canyons and other formations. Then the ice dam was created again and broke again and created again and broke again. This cycle happened at least 15 times, depending on who you talk to, starting about 16,000 years ago. It explains the modern geology of Central Washington state’s coulees (those carved canyons), potholes, dry waterfalls, and so-called Scablands. You can read more about this in Wikipedia. Or you can just watch the documentary I’m reviewing here.
The best way to get an idea of the massive scale of the hydrologic action resulting from the Floods is from the air. Sure, you can take a hike into a coulee or to the top of Dry Falls and look around, but it isn’t until you get a few hundred feet up that you realize just how enormous these places are. So the film crew looked for a helicopter with a Cineflex camera mount. Of course, there aren’t any of those outside a big city and they did have a budget so bringing one in was not an option. They did, however, find my helicopter company, Flying M Air, which, at the time, owned a Moitek gyrostabilized camera mount (which I’ve since sold).
I should mention here that this is the one and only time that damn camera mount got me a flying gig. I bought it to increase my aerial photo business and very seldom used it. I charged a fee for its use and it probably finally paid for itself sometime in 2014; I’d owned it since 2009. It was a beautiful piece of equipment, exquisitely hand made right here in Washington State, but it weighed a ton and took 30 minutes to assemble and another 20 minutes to break down. I hated dealing with it, despite the $500 per use fee I charged. Packed in two huge Pelican cases — one for the mount itself and one for the three Kenyon KS-8 gyros that went with it — it took up space and gathered dust on my garage floor. I sold it to an LA-based pilot for just $5K this past summer. What a steal. The gyros alone were worth more than that — but I don’t miss it one damn bit. It was not one of my best asset acquisition decisions.
The Flights
Turns out that they needed a videographer who could use the mount and had appropriate equipment to mount on it. I turned to Charley Voorhis of Voortex Productions, one of the two local video companies I’ve worked with. Charley has some impressive equipment — I think he brought one of his RED cameras for this gig — and lots of experience with the mount. (I almost wish he’d bought it.) Then I stepped back and let him make his deal with the client. All I cared about was flying.
The day of the flight came and we left, bright and early, for Spokane. I’d already set up the mount as far as I could, tying it down with gaffer tape since it would be out of balance until a camera was on it. I’d put the door back on so we could maximize cruise speed to get to the client meeting site; the helicopter is limited to 100 knots with any door off. We got there on time and met at the FBO to come up with a plan. I had them top off the tanks with fuel and removed the door where the camera mount was. Charley set up his camera.
We wound up doing several flights. The first was a long one that started in Spokane, flew directly out to Dry Falls — which is about 2/3 of the way back to Wenatchee — circled that more times than I can count, and then headed down the smaller lakes to Ephrata, past Moses Lake, and over the Potholes Reservoir. On board were me (of course), Charley, and the video director (or producer?) who told Charley what shots to get. The mount took up a whole seat but I wouldn’t have taken a third passenger if I could; I have a strict policy regarding the number of people on board for photo flights and always limit it to three.
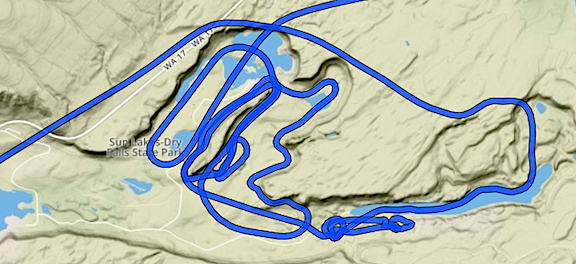
Here’s a closeup of my track, recorded automatically by ForeFlight, for the time we were in the Dry Falls area. What’s ironic here is that we flew around in a noisy helicopter for a good 15 minutes and likely bugged the hell out of people on the ground. A drone probably could have gotten the same footage without disturbing so many people. (Of course, it would have taken most of the day.) But because Dry Falls is a Washington State Park, drones are prohibited. Go figure, huh?
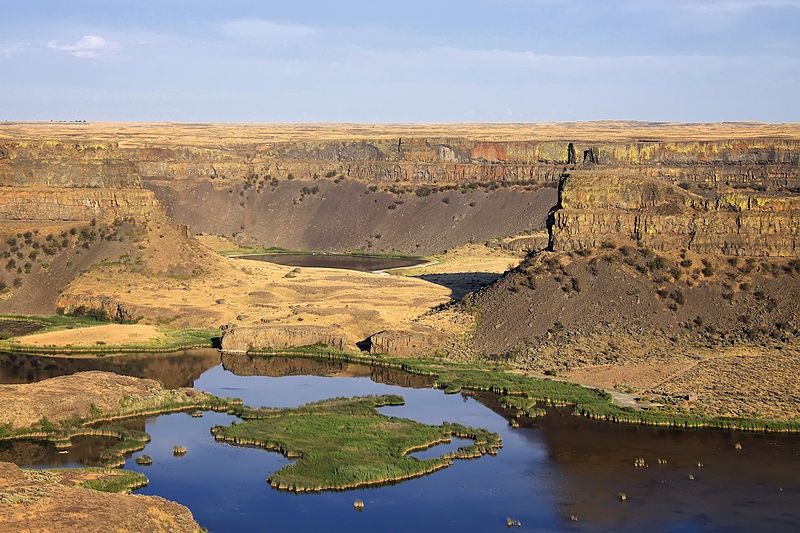

Photo of Dry Falls by © Steven Pavlov / http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Senapa, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=16059590 I think that most of the footage shot from my helicopter and used in the documentary was shot in this area.
After refueling at Moses Lake — we’d flown about 2-1/2 hours since leaving Spokane — we pretty much high-tailed it back to Spokane. Then we did two flights south past Cheney and east of Ritzville. That’s where the Drumheller Channels are. I’d never even heard of the place, but apparently it’s one of the best examples of the Channeled Scablands. One flight was with the same group on board; the other was with the geologist you see in the documentary. When the geologist was on board, the client’s own videographer flew with me, sitting beside me to shoot the geologist in the seat behind me as he spoke about what we were flying over. That’s probably also when they got footage of my helicopter’s panel and even me. Those two flights each took about a 1-1/2 hours with refueling in Spokane between each one.
After that, we were done. I dropped everyone off in Spokane, retrieved the door, and put it back on. Charley and I sped back to Wenatchee where we went our separate ways.
I think the whole gig was supposed to be just 5 hours, including travel time, but I flew (and billed for) more than 9. It was a very lucrative gig. But what was [almost] better was how much I saw and learned about the geology of the state. That’s one of the reasons I like doing aerial photo work; I get to see and learn a lot.
The Documentary
I have to admit that once my invoice was paid — which took a little effort since the money was coming from the UK — I didn’t give the project much thought. I didn’t even blog about it. That’s probably because last summer was very busy for me and I did a lot of cherry drying work. I even dried cherries later that day. I’d stopped blogging about my interesting flights, although I really don’t know why.
So imagine my surprise when a lawyer friend asked me yesterday in an email if he’d just seen my helicopter in a NOVA episode.
I went online and found the NOVA episode titled Killer Floods immediately. And although I rarely watch television during the day, I’m recovering from a cold and figured it was a good way to kill an hour. So I sat down, fired up the Roku with PBS, and watched it.
Let me start by saying I generally like NOVA documentaries. At least I used to. They’re filled with facts and good videography and leave you feeling better educated about topics than you were before you watched them. But I don’t know if it’s a general trend in documentary filmmaking or just a new NOVA style, but it seems to me that they’re trying too hard to sensationalize the topic or apply it to today’s world.
Two things immediately struck me about this one.
First, the name: Killer Floods. This particular documentary covered three flood events, all three of them were prehistoric. So although it’s likely that they killed something — plants? animals? — they didn’t have an impact on man at the time. In addition, their significance was not the fact that things were killed but more that the flooding changed the shape of the landscape by suddenly and violently eroding and washing away rock.
Second, the attempt to suggest that the three floods documented in the video have anything whatsoever to do with today’s flooding due to climate change. They managed to include footage from the flooding in Houston from Hurricane Harvey — a mere two months before air time! — which has absolutely nothing to do with these three prehistoric floods. Yet the narrator suggested that they might be related. I think that’s stretching it beyond reasonability.
But hey — I get it. They want people to watch so they come up with sensationalized names (see also Killer Hurricanes and Killer Volcanoes), and try to get people interested by pointing to recent events that they’re familiar with. After all, is the average person going to be interested in a documentary about how three prehistoric flood events changed the landscape in relatively remote areas of Central Washington State and Iceland or under the English Channel? I doubt it. NOVA is competing with reality TV, sitcoms, and sports. While I’m interested in just about any topic NOVA covers, most people aren’t. Sad but true.
That said, I thought the documentary was well written and produced, with plenty of good videography, interview clips, and narration. It walked viewers through the logical process of figuring out how each of the three landscape formations they were researching were actually made. (I already explained the one in Washington State; I’ll let you watch the documentary to learn about the other two.) The Washington one was a bit slow for me because I already knew the answer but I found the other two fascinating. I’ve been planning a trip to Iceland for late next summer and may extend it a few days to take in some of the sights shown in the documentary. And now I have a fresh desire to see the White Cliffs of Dover.
But what really tickled me was seeing my helicopter near the very beginning of the documentary, with the Flying M Air logo prominently displayed. Later, a shot shows my door with my name on it. And somewhere else near the beginning, you can see the helicopter’s controls and even a quick shot of me looking like a bit of a bum in my gray sweatshirt.
Those glimpses were enough to get my brother, who never picks up the phone, to give me a call yesterday evening. “I’m watching NOVA. Is that your helicopter?”
And that set off an hour-long conversation about all kinds of things. Heck, I talked more with him yesterday evening than I had all of last year. (Seriously: he just doesn’t like to talk on the phone.)
This obviously isn’t the first time I’ve been involved in a video production. I’ve been flying this helicopter since 2005 and have done countless video/photo shoots over the past 13 years. But I’m pretty sure this is the first one that has appeared on PBS or a highly respected documentary series like NOVA.
It’s about as “big time” as my little company will get — and that’s okay with me.
If you’re going to watch it, watch it soon. The website says it “expires” on December 7. If you’re really interested in flood-related geology, why not get the video? You can buy it on iTunes.
Look for me in the credits.





