I see the aurora for the first time — well, sort of — right from the comfort of my own home.
If you pay attention at all to science-related news, you are probably aware that the sun is near the peak of its 11-year solar activity cycle, with lots of sunspots and coronal mass ejections. This has made aurora a lot more visible than usual, making it possibly for people to see it as far south as Arizona and Texas.
I don’t live that far south. I live in north central Washington state. Opportunities to view the aurora abound at my home — which has a perfectly unobstructed view to the north, right to the horizon — but I’ve spent much of the past two years away from home. Ironically, from June through August, I was traveling at latitudes farther north than where my home is, but I just didn’t see the aurora on any nights I might have. I could blame weather (clouds), ambient lighting (being near a city), or a lack of clear view to the north (from trees or mountains).
But when I got home, I became determined to see the aurora from my home.
The Science of the Aurora
I would be remiss if I did not mention the excellent Space Weather and Aurora Dashboard pages constantly updated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). It provides a wealth of information about the aurora, from forecasts and current conditions to basic and detailed information about what causes the aurora.
For example, NOAA’s Aurora Tutorial page starts its explanation of the aurora like this:
The aurora is formed from interactions between the solar wind streaming out from the sun and Earth’s protective magnetic field, or magnetosphere. The aurora is one manifestation of geomagnetic activity or geomagnetic storms. As the solar wind increases in speed and the interplanetary magnetic field embedded in the solar wind turns southward, the geomagnetic activity will increase and the aurora will become brighter, more active, and move further from the poles. Even moderate solar wind creates aurora so there is usually a weak aurora somewhere even when there isn’t a big geomagnetic storm.
There are two types of solar events that create big geomagnetic storms that are associated with bright and active aurora. The first is a Coronal Mass Ejection, or CME, which can be described as a billion tons of plasma ejected from the sun, traveling at a million miles per hour. When a CME arrives at Earth, it can produce some of the biggest geomagnetic storms and thus, some of the brightest and most active auroras that extend furthest toward the equator. The second solar event that can create moderate sized geomagnetic storms is called a coronal hole. Coronal holes are the source of high speed solar wind streams. When these high speed streams arrive at Earth, they can produce active auroras. But the geomagnetic storms and aurora associated with coronal holes is less active than those from the biggest and fastest CME’s.
Later on that page, it explains what causes the individual colors you might see. This is a great place to start if you want to learn more about how the aurora forms and when viewing is best.
Forecasts < Actual Conditions
My quest to see the aurora started with the forecasts on the Aurora Dashboard page. Each day, NOAA provides a forecast for tonight and tomorrow night. You can see an example in the top two images in the screen capture below. Like any weather forecast, this is a prediction of what might happen based on data and models. In this particular example, the forecast looked good for two nights in a row.
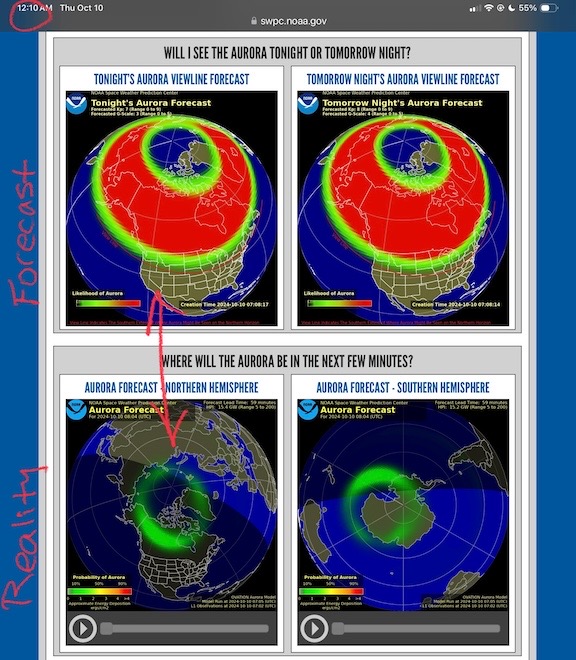
In the early morning hours of October 10, the forecast for that night was a lot more optimistic than reality.
I’ve lost a lot of sleep trying to see the aurora. In this example, the forecast told me it should be visible where I live. But this page also provides a very short term forecast for the next 35 minutes. The image on the left is for the northern hemisphere and it painted a truer picture of the situation. The chances of seeing the aurora where I lived was slim. And, of course, I didn’t see it on the night of October 9-10.
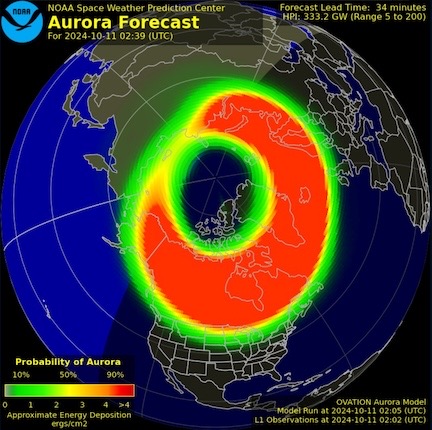
The short term forecast looked a lot better on the night of October 10-11.
But things were different on the night of October 10-11. I knew they were different when my social media feed on Mastodon began filling with aurora photos. I watched the Aurora Dashboard and was rewarded with a very promising short term forecast image. I set up a GoPro pointed mostly at the northern horizon and sky and turned on the night hyperlapse feature. Then I turned off all the lights in my home, including the solar string lights on my deck, and hung out on the deck to watch the sky.
Understand that my home might be 2 miles down a gravel road 10 miles from town, but it has a commanding view of the entire valley, including the brightly lighted cities of Wenatchee and East Wenatchee. This is not a good place for stargazing. No matter how much I tried to get my eyes adjusted to the dark, it simply wasn’t dark. But soon, after a while, I started seeing a reddish glow in the sky. I took a photo with my iPhone 13 Pro — yes, I know it’s time for an update; maybe after Christmas — and was shocked to see auroral streaks of pink lines in the photo.
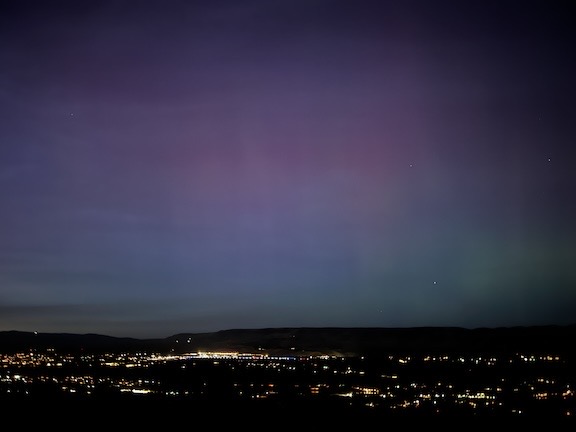

This was the first photo I took from my deck. It was 7:13 PM, less than an hour after sunset.
For the next few hours, I moved from inside my nice warm (but dark) house to outside on my cool deck. I tried hard to see beyond the faint streaks in the sky, but every time I took a photo, the photo revealed far more than I was seeing. It was out there but my eyes just couldn’t take in enough auroral light to see it very well.
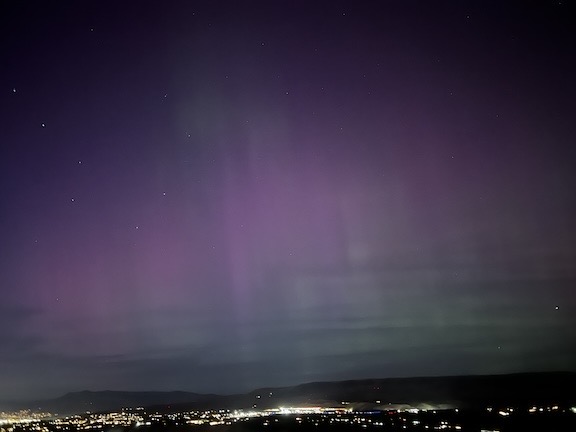

I took this photo a little while later. The predominant colors were a pink and an almost lime green.
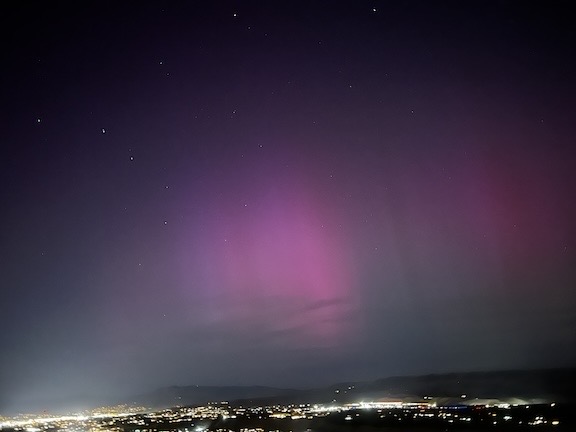

Here’s another shot from a while later.
It was rewarding but also frustrating. This was probably the first time in my life when I could photograph something better than I could see it. But I wanted to see it! With my eyes!
The sky started to cloud up a little and my frustration got the better of me. After a while, I gave up.
The Video
This was apparently a mistake. I should have tried again around midnight. How do I know this? Well, remember that GoPro I set up? Here’s what it captured before its battery died:
The Next Aurora Viewing
I’m watching the forecast pages closely. The next time we have a strong forecast, I’ll be ready with multiple cameras — including my Nikon, on a tripod — to capture it. But next time, I’ll set up a lounge chair on the deck, snuggle in a sleeping bag, and watch until I can see it better with my own eyes.



